How do predicted pKa and solubility values compare to reality?
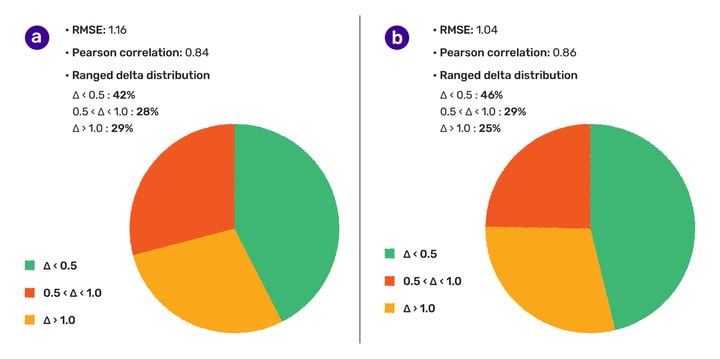
The accuracy of the pKa prediction tool was evaluated on a drug discovery set, yielding an RMSE of 1.11 and a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.88. The solubility predictor was also assessed on a dataset containing rare elements, multi-component structures, and quaternary nitrogen atoms, achieving an RMSE of 1.16 and a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.84. A ligand preparation was carried out to filter out structures outside the applicability domain, resulting in higher accuracy on the subset counting 6886 cases. The study aims to provide transparency for the user community and trigger discussions, while also improving the model by training on previously unseen chemical spaces. The authors are open to collaborations with contributors who can share experimentally determined phys-chem data.
Accurate calculated molecular properties have a high impact on understanding relationships with measured attributes of the compounds, training models for new targets and predicting characteristics of novel entities. Chemaxon predictions, especially molecular features with higher complexity like ionization, lipophilicity or solubility are well accepted and widely used both in industry settings and academic research. During the development of these algorithms, continuous accuracy assessment is part of our strategy. In order to make this step automatic, reproducible and transparent we built a small bit of code to generate accuracy reports and publish them.
First, we evaluated the pKa prediction tool on a drug discovery set disclosed by AstraZeneca (ChEMBL assay ID: CHEMBL3301362). In this data set the most basic pKa value was determined by absorption and potentiometric titration using standard methodology from Sirius Analytical for 261 compounds. Out of them 12 had no value, 2 experiments were presented with > relation and 4 compounds did not have predicted pka value in 0-14 range. On the final set (243 cases), the off-the-shelf prediction yielded an RMSE of 1.11, and a Pearson correlation coefficient (r) of 0.88 (Fig 1.).
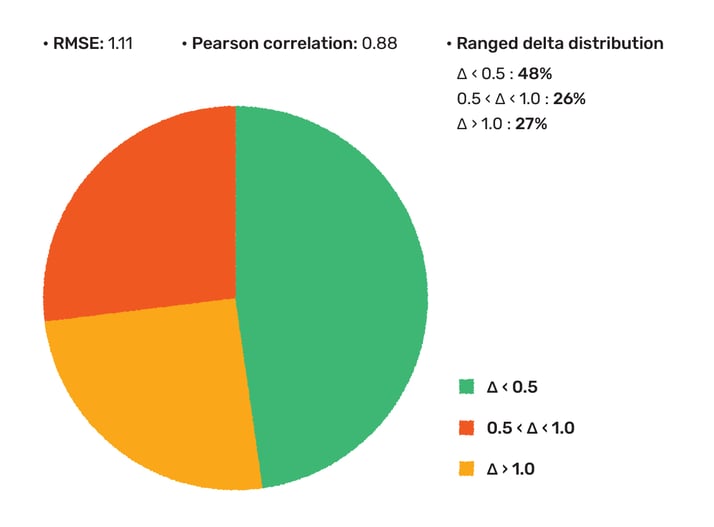 Figure 1. Basic pKa accuracy assessment on CHEMBL3301362 assay data.
Figure 1. Basic pKa accuracy assessment on CHEMBL3301362 assay data.
48% of the measured values were predicted within 0.5 pKa unit, and 73% was within 1 pKa. The report that has been uploaded to the documentation page and is also available here.
We were also interested in how accurate our solubility predictor is, thus we picked a dataset that was recently published by Hongping Zhao et al. (DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00121). The standard intrinsic solubility model achieved 1.16 RMSE and 0.84 Pearson correlation coefficient (r) on these 9390 structures. 42% of the cases were predicted within 0.5 logS unit, and 71% was within 1 logS unit (Fig. 1.). During the analysis of the chemical space, we recognized that this set contains rare elements, quaternary nitrogen atoms and multi-component structures that are falling out of the scope of the designed applicability domain of the solubility predictor. Therefore, a ligand preparation was carried out to eliminate multi-component, permanently charged molecules and structures containing rare elements.
On the subset counting 6886 cases, a bit higher accuracy (RMSE:1.04, Pearson correlation coefficient (r) 0.86, 46% and 75% of cases within 0.5 and 1 logS unit, respectively) was observed.
Considering that the 1 log unit (logS or pKa) corresponds to 5.9 kJ/mol free energy change, the observed 1 RMSE, or median delta ~0.5, can be considered as an accurate prediction to support novel compound design. However, we are interested in improving our model by training on previously unseen chemical spaces. We are open to contributors who can share experimentally determined phys-chem data. Find us to start a discussion on collaboration, fair compensation and more.
This small study had two aspects: (i) Provide higher transparency for the user community on the applicability and prediction power of our tools and trigger discussion. (ii) Extend the package with automatic QC analysis capability for model training use-case and each assessment and new data point triggers us to improve. We can evaluate the second and ask you to tell us your opinion on the first.